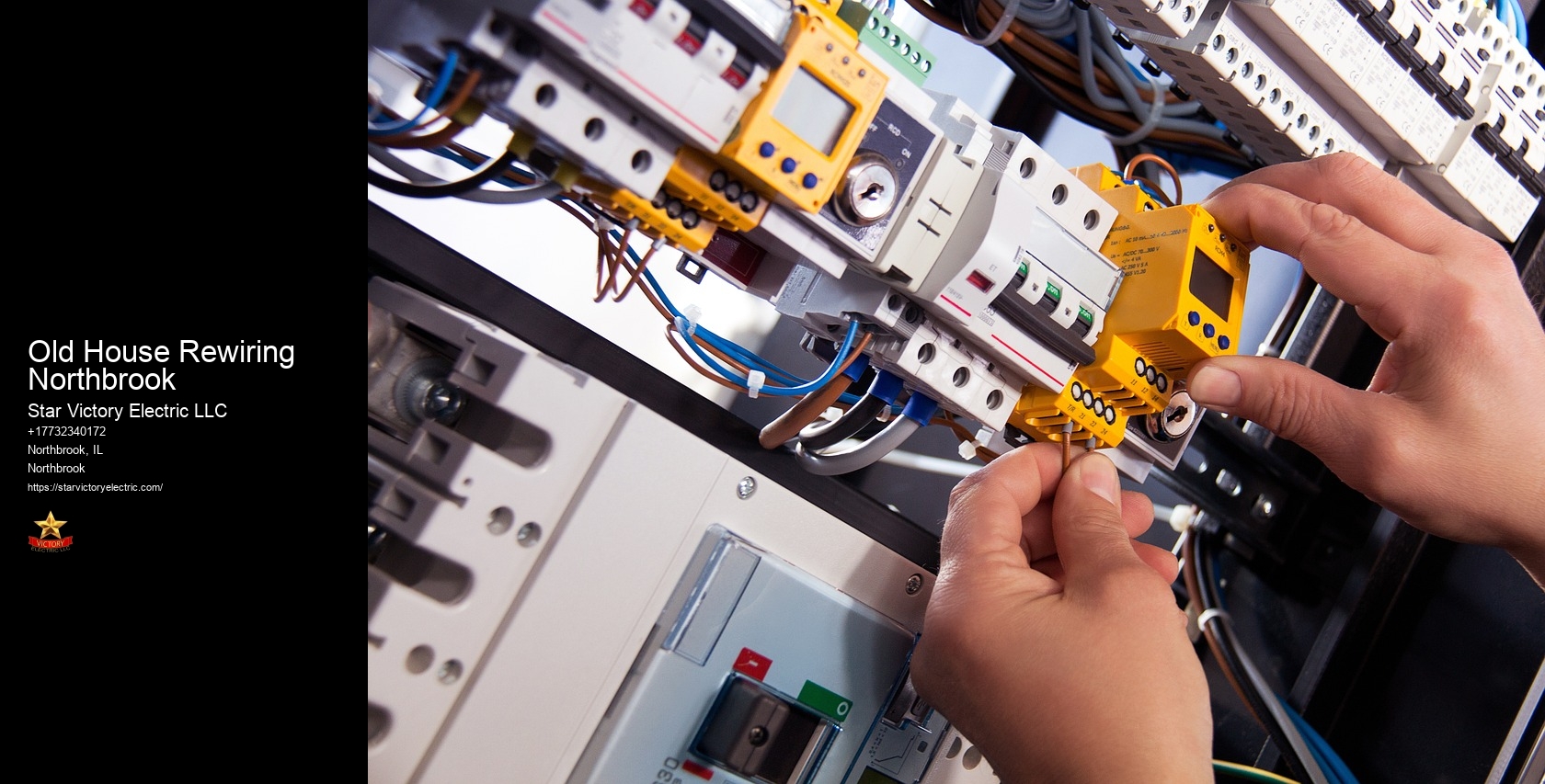

Over time, wiring can deteriorate, connections may loosen, and your once state-of-the-art system could become a safety hazard. Whether it's a power outage, a flickering light, or something more serious, their team is just a phone call away. Learn more about Old House Rewiring Northbrook here Moreover, by offering educational resources and an unwavering emergency response commitment, they empower residents with knowledge and confidence. Stay with us as we shed light on what makes Star Victory Electric a shining example of excellence in a competitive field. You'll often find their team at local events, from sponsoring youth sports leagues to participating in town clean-up days.
You'll find they're not only keeping up with the latest electrical codes and standards but also diving into the newest technologies in the electrical field. Whether you're facing a sudden power outage, a tripped breaker that won't reset, or you've noticed a burning smell coming from an outlet, you're just a phone call away from a solution. You'll find their team hosting free workshops and seminars aimed at teaching homeowners the basics of electrical safety, how to recognize potential hazards, and the steps to take if they encounter an electrical issue. Choosing us means you're partnering with a company that values safety, quality, and customer satisfaction above all else. Learn more about Star Victory Electric LLC here.
They've committed themselves to being your first line of defense, ensuring that help is on its way whenever you need it. After completing a job, they'll check in to ensure everything meets your expectations. Their commitment to innovation means your home isn't just powered; it's empowered.
Moreover, insurance plays a critical role in protecting both you and the electrician. That's why we offer transparent pricing, efficient service, and follow-up support to address any concerns you might've post-service. You'll find that their professionals hold certifications from recognized institutions, ensuring a high level of proficiency and knowledge. Moreover, their proactive maintenance services help in identifying and fixing any potential issues before they become major problems.
And it's not just about adding new gadgets. From the very start, they set out to make electrical services safer, more reliable, and accessible to homeowners in Northbrook and beyond. Whether you're in need of comprehensive services, from minor installations to major electrical overhauls, or you're looking for a team that values its local community as much as you do, there's a reason Star Victory Electric LLC has become a household name. Recognizing the evolving landscape of technology and home automation, we've expanded our repertoire to include smart home installations and energy-efficient lighting solutions.
As word of mouth spread, you'd hear more and more Northbrook residents turning to Star Victory Electric for their electrical needs. They transformed the old electrical infrastructure into a modern, energy-efficient marvel, ensuring that each store wasn't only well-lit but also environmentally conscious. With Star Victory Electric LLC, you're not just getting a service; you're getting a partner committed to the safety and efficiency of your home's electrical system.
They understand that major renovations aren't just about aesthetics; they're about ensuring your electrical system can support your home's new demands safely and efficiently. They've not only kept pace with the evolving technology but have led the way in adopting sustainable and efficient electrical solutions. Read more about Old House Rewiring Northbrook here But what exactly makes Star Victory Electric stand out from the rest, and how have they earned such high praise from your neighbors?
At Star Victory Electric LLC, your peace of mind is our victory. You'll find comfort in knowing that Star Victory Electric's emergency services are available 24/7. Their expert electricians also listen to your concerns, whether it's flickering lights or a desire to modernize your home's electrical system.


In Northbrook, this isn't just an expectation; it's a standard. Simple habits like not overloading outlets, keeping water away from electrical appliances, and using extension cords wisely can prevent mishaps. If you encounter flickering lights, a sparking outlet, or any other sign of an electrical problem, don't hesitate to reach out. By their 20th year, they'd expanded their services to include not only residential but also commercial and industrial projects, significantly broadening their scope and expertise. As they mark this milestone, it's not just about reflecting on past achievements but also looking ahead.
They understand that your home's electrical system plays a significant role in your overall energy consumption. They know that your home's electrical system is crucial for your comfort and safety, so they listen closely to your needs and preferences right from the start. They're also your go-to for smart home integrations, energy-efficient lighting solutions, and electrical panel upgrades. It's about safeguarding your home, protecting your loved ones, and ensuring your electrical system is up to the task.
If you prefer digital communication, their website offers a convenient contact form. Charging station Star Victory Electric LLC equips its professionals with the latest safety gear to protect both them and your home during electrical work. Their technicians aren't just skilled; they're licensed, insured, and continuously trained on the latest electrical codes and technologies. Star Victory Electric provides a wide range of electrical services to meet all your needs, from simple repairs to complex installations.
You might think that finding a reliable electrical service that excels in both repairs and installations is a tall order, but Star Victory Electric LLC in Northbrook is a game changer in this respect. They conduct a thorough analysis to identify underlying issues that could cause future failures or safety hazards. Prioritizing your safety, Star Victory Electric LLC adheres to rigorous safety standards and practices in every project. They conducted thorough safety checks before starting any work and explained what they were doing in simple terms.
Their team is equipped to handle installations both big and small, ensuring your home's electrical systems are modern, efficient, and safe. So, when it comes to keeping your home powered safely and efficiently, they're not just your electricians – they're your partners in home maintenance. They can upgrade your home to accommodate more energy-efficient appliances, install smart home technology, and ensure your electrical system meets current safety standards. Each member isn't just skilled but also certified, ensuring they're up-to-date with the latest electrical codes and safety standards. Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected failures and prolong the life of your electrical systems, saving you money and hassle in the long run.
From simple repairs to complex installations, you're in capable hands. And let's not forget the hard hats. We understand that electrical upgrades and maintenance in your home aren't just about the technical work; it's also about minimizing disruption to your daily life. But what is it about their approach that ensures your peace of mind and keeps your home running smoothly?
To further empower the Northbrook community, Star Victory Electric LLC offers a variety of educational resources on electrical safety. This step ensures we're fully prepared to meet your needs on the day of service. Then there's Jamie, the project manager, known for her meticulous planning and exceptional customer service. They're also pioneering the installation of solar panels and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations.
Choosing Star Victory Electric LLC means you're opting for reliability. This initiative not only showcases their dedication to community safety but also builds a foundation of trust and reliability with residents. You're a part of creating a safer, smarter home environment. They wore protective gear and used the latest tools to ensure a safe repair.
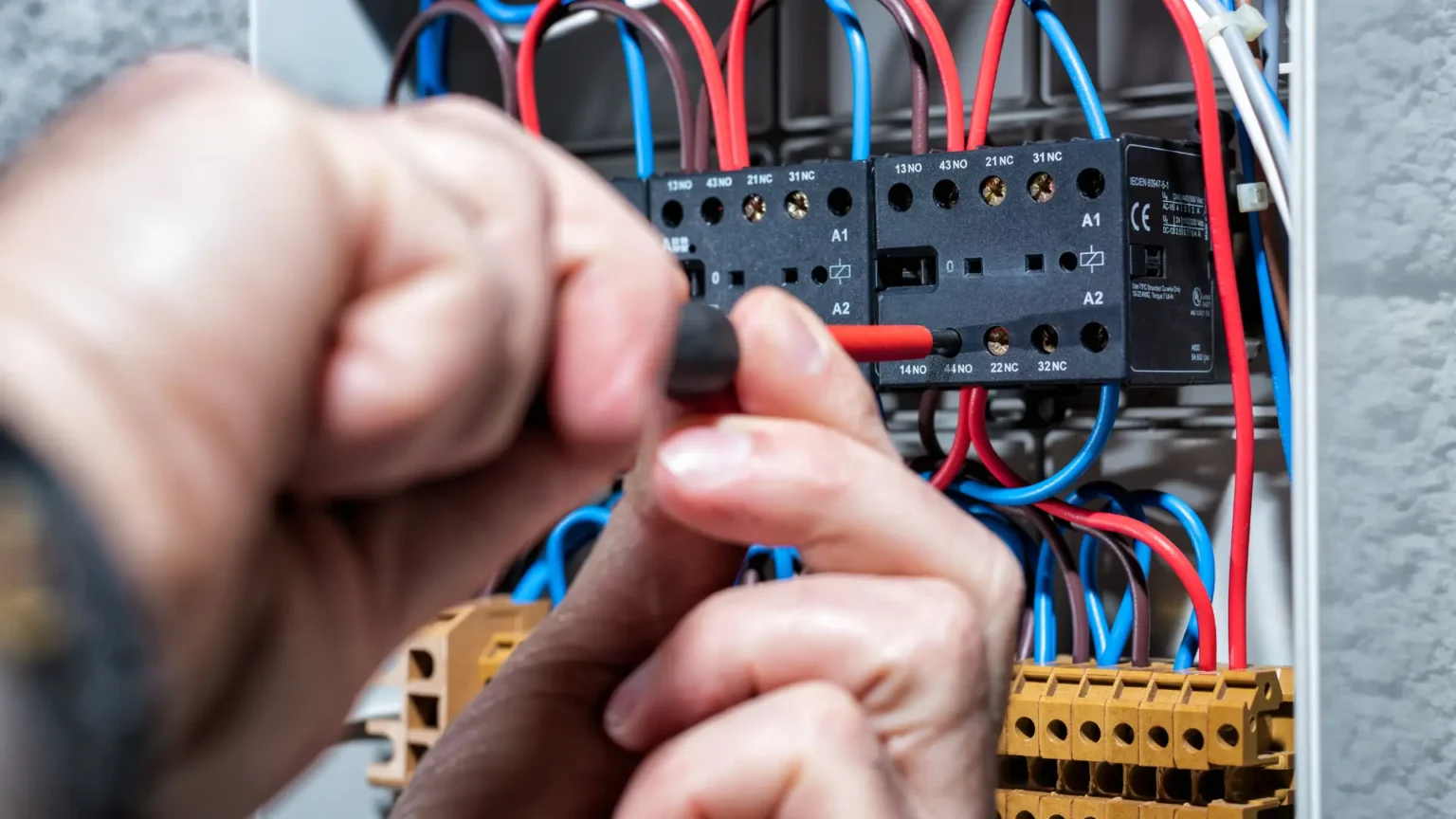

They understand that electrical work isn't just about ensuring the lights turn on or the appliances work; it's about making sure your home is safe from electrical hazards that can lead to fires or electrocution. From surge protectors that keep your tech safe during a storm to dedicated circuits that prevent overloads, every recommendation is about keeping you and your home safe. Whether you're in the midst of a remodel, looking to upgrade your home's electrical system, or simply need maintenance or repairs, they've got you covered. This isn't just for compliance; it's a critical measure to identify and rectify potential hazards before they escalate. These changes can drastically reduce your electricity bills and are better for the environment.
They're not just about wires and circuits; they're about people. Moreover, their transparent pricing policy means you won't be caught off guard by unexpected costs. By ensuring your home's electrical system is up to code, you're minimizing these risks significantly. As you navigate the complexities of modern home electrification, the significance of partnering with a provider that combines comprehensive service offerings with an expert team cannot be understated.
Their commitment doesn't stop there. Star Victory Electric's commitment to excellence means you're getting more than just a service; you're getting peace of mind. We also use advanced testing tools to ensure circuits are dead before we start working, preventing accidental shocks. We've also introduced comprehensive electrical safety inspections and energy audits, aimed at ensuring your home isn't only safe but also running as efficiently as possible.
One of their most challenging projects was the overhaul of the Northbrook High School's electrical system. That's why they're not just focused on getting the job done; they're committed to doing it right, prioritizing your safety above all else. At the heart of Star Victory Electric LLC's success are its core values and mission, guiding every project and customer interaction with integrity and dedication. They're not just about keeping the lights on; they're transforming how you interact with your home.
We understand that you're not just looking for electrical services; you're seeking a partner you can trust to keep your home safe and functional. They understand the importance of giving back. You'd be impressed by their investment in energy-efficient technologies, from LED lighting in offices to electric vehicles in their service fleet. Instead, Star Victory Electric ensures you're directly connected with knowledgeable staff ready to address your concerns.
Moreover, Star Victory Electric LLC collaborates with local schools to introduce electrical safety to students. Our electricians regularly attend workshops and continue their education to stay ahead of industry standards and technologies. They're not just electricians; they're guardians of electrical safety.
You can trust them to use the best materials, adhere to the strictest safety standards, and pay attention to every detail. As you stand on the brink of understanding the electrifying journey of Star Victory Electric, it's like peering into the intricate wiring behind a well-lit home. These experts aren't just skilled; they're also continually trained to stay ahead of the latest industry standards and technologies.
They knew the value of trust and reliability in their line of work, and they set out to embed these values into the fabric of their operations. Moreover, they're adept at installing GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets in high-risk areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoors. They don't just meet the minimum safety requirements; they aim to exceed them, providing you with service that's as reliable as it's secure.

|
|
The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the English-speaking world and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (March 2025)
|

|
|
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
|
Occupation type
|
Vocational |
|
Activity sectors
|
Maintenance, Electrical Grid |
| Description | |
|
Education required
|
Apprenticeship |
|
Fields of
employment |
Construction |
|
Related jobs
|
Lineperson |
An electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical infrastructure.[1] Electricians may also specialize in wiring ships, airplanes, and other mobile platforms, as well as data and cable lines.
Electricians were originally people who demonstrated or studied the principles of electricity, often electrostatic generators of one form or another.[2]
In the United States, electricians are divided into two primary categories: lineperson, who work on electric utility company distribution systems at higher voltages, and wiremen, who work with the lower voltages utilized inside buildings. Wiremen are generally trained in one of five primary specialties: commercial, residential, light industrial, industrial, and low-voltage wiring, more commonly known as Voice-Data-Video, or VDV. Other sub-specialties such as control wiring and fire-alarm may be performed by specialists trained in the devices being installed, or by inside wiremen.
Electricians are trained to one of three levels: Apprentice, Journeyperson, and Master Electrician. In the US and Canada, apprentices work and receive a reduced compensation while learning their trade. They generally take several hundred hours of classroom instruction and are contracted to follow apprenticeship standards for a period of between three and six years, during which time they are paid as a percentage of the Journeyperson's pay. Journeymen are electricians who have completed their Apprenticeship and who have been found by the local, State, or National licensing body to be competent in the electrical trade. Master Electricians have performed well in the trade for a period of time, often seven to ten years, and have passed an exam to demonstrate superior knowledge of the National Electrical Code, or NEC.
Service electricians are tasked to respond to requests for isolated repairs and upgrades. They have skills troubleshooting wiring problems, installing wiring in existing buildings, and making repairs. Construction electricians primarily focus on larger projects, such as installing all new electrical system for an entire building, or upgrading an entire floor of an office building as part of a remodeling process. Other specialty areas are marine electricians, research electricians and hospital electricians. "Electrician" is also used as the name of a role in stagecraft, where electricians are tasked primarily with hanging, focusing, and operating stage lighting. In this context, the Master Electrician is the show's chief electrician. Although theater electricians routinely perform electrical work on stage lighting instruments and equipment, they are not part of the electrical trade and have a different set of skills and qualifications from the electricians that work on building wiring.
In the film industry and on a television crew the head electrician is referred to as a Gaffer.
Electrical contractors are businesses that employ electricians to design, install, and maintain electrical systems. Contractors are responsible for generating bids for new jobs, hiring tradespeople for the job, providing material to electricians in a timely manner, and communicating with architects, electrical and building engineers, and the customer to plan and complete the finished product.


Many jurisdictions have regulatory restrictions concerning electrical work for safety reasons due to the many hazards of working with electricity. Such requirements may be testing, registration or licensing. Licensing requirements vary between jurisdictions.
An electrician's license entitles the holder to carry out all types of electrical installation work in Australia without supervision. However, to contract, or offer to contract, to carry out electrical installation work, a licensed electrician must also be registered as an electrical contractor. Under Australian law, electrical work that involves fixed wiring is strictly regulated and must almost always be performed by a licensed electrician or electrical contractor.[3] A local electrician can handle a range of work including air conditioning, light fittings and installation, safety switches, smoke alarm installation, inspection and certification and testing and tagging of electrical appliances.
To provide data, structured cabling systems, home automation & theatre, LAN, WAN and VPN data solutions or phone points, an installer must be licensed as a Telecommunications Cable Provider under a scheme controlled by Australian Communications and Media Authority[4]
Electrical licensing in Australia is regulated by the individual states. In Western Australia, the Department of Commerce tracks licensee's and allows the public to search for individually named/licensed Electricians.[5]
Currently in Victoria the apprenticeship lasts for four years, during three of those years the apprentice attends trade school in either a block release of one week each month or one day each week. At the end of the apprenticeship the apprentice is required to pass three examinations, one of which is theory based with the other two practically based. Upon successful completion of these exams, providing all other components of the apprenticeship are satisfactory, the apprentice is granted an A Class licence on application to Energy Safe Victoria (ESV).
An A Class electrician may perform work unsupervised but is unable to work for profit or gain without having the further qualifications necessary to become a Registered Electrical Contractor (REC) or being in the employment of a person holding REC status. However, some exemptions do exist.[6]
In most cases a certificate of electrical safety must be submitted to the relevant body after any electrical works are performed.
Safety equipment used and worn by electricians in Australia (including insulated rubber gloves and mats) needs to be tested regularly to ensure it is still protecting the worker. Because of the high risk involved in this trade, this testing needs to be performed regularly and regulations vary according to state. Industry best practice is the Queensland Electrical Safety Act 2002, and requires six-monthly testing.

Training of electricians follows an apprenticeship model, taking four or five years to progress to fully qualified journeyperson level.[7] Typical apprenticeship programs consists of 80-90% hands-on work under the supervision of journeymen and 10-20% classroom training.[8] Training and licensing of electricians is regulated by each province, however professional licenses are valid throughout Canada under Agreement on Internal Trade. An endorsement under the Red Seal Program provides additional competency assurance to industry standards.[9] In order for individuals to become a licensed electricians, they need to have 9000 hours of practical, on the job training. They also need to attend school for 4 terms and pass a provincial exam. This training enables them to become journeyperson electricians. Furthermore, in British Columbia, an individual can go a step beyond that and become a "FSR", or field safety representative. This credential gives the ability to become a licensed electrical contractor and to pull permits. Notwithstanding this, some Canadian provinces only grant "permit pulling privileges" to current Master Electricians, that is, a journeyperson who has been engaged in the industry for three years and has passed the Master's examination (i.e. Alberta). The various levels of field safety representatives are A, B and C. The only difference between each class is that they are able to do increasingly higher voltage and current work.
The two qualification awarding organisations are City and Guilds and EAL. Electrical competence is required at Level 3 to practice as a 'qualified electrician' in the UK. Once qualified and demonstrating the required level of competence an Electrician can apply to register for a Joint Industry Board Electrotechnical Certification Scheme card in order to work on building sites or other controlled areas.
Although partly covered during Level 3 training, more in depth knowledge and qualifications can be obtained covering subjects such as Design and Verification or Testing and Inspection among others. These additional qualifications can be listed on the reverse of the JIB card. Beyond this level is additional training and qualifications such as EV charger installations or training and working in specialist areas such as street furniture or within industry.
The Electricity at Work Regulations are a statutory document that covers the use and proper maintenance of electrical equipment and installations within businesses and other organisations such as charities. Parts of the Building Regulations cover the legal requirements of the installation of electrical technical equipment with Part P outlining most of the regulations covering dwellings
Information regarding design, selection, installation and testing of electrical structures is provided in the non-statutory publication 'Requirements for Electrical Installations, IET Wiring Regulations, Eighteenth Edition, BS 7671:2018' otherwise known as the Wiring Regulations or 'Regs'. Usual amendments are published on an ad hoc bases when minor changes occur. The first major update of the 18th Edition were published during February 2020 mainly covering the section covering Electric vehicles charger installations although an addendum was published during December 2019 correcting some minor mistakes and adding some small changes. The IET also publish a series of 'Guidance Notes' in book form that provide further in-depth knowledge.
With the exception of the work covered by Part P of the Building Regulations, such as installing consumer units, new circuits or work in bathrooms, there are no laws that prevent anyone from carrying out some basic electrical work in the UK.
In British English, an electrician is colloquially known as a "spark".[10]

The United States does not offer nationwide licensing and electrical licenses are issued by individual states. There are variations in licensing requirements, however, all states recognize three basic skill categories: level electricians. Journeyperson electricians can work unsupervised provided that they work according to a master's direction. Generally, states do not offer journeyperson permits, and journeyperson electricians and other apprentices can only work under permits issued to a master electrician. Apprentices may not work without direct supervision.[11]
Before electricians can work unsupervised, they are usually required to serve an apprenticeship lasting three to five years under the general supervision of a master electrician and usually the direct supervision of a journeyperson electrician.[11] Schooling in electrical theory and electrical building codes is required to complete the apprenticeship program. Many apprenticeship programs provide a salary to the apprentice during training. A journeyperson electrician is a classification of licensing granted to those who have met the experience requirements for on the job training (usually 4,000 to 6,000 hours) and classroom hours (about 144 hours). Requirements include completion of two to six years of apprenticeship training and passing a licensing exam.[12]
An electrician's license is valid for work in the state where the license was issued. In addition, many states recognize licenses from other states, sometimes called interstate reciprocity participation, although there can be conditions imposed. For example, California reciprocates with Arizona, Nevada, and Utah on the condition that licenses are in good standing and have been held at the other state for five years.[13] Nevada reciprocates with Arizona, California, and Utah.[14] Maine reciprocates with New Hampshire and Vermont at the master level, and the state reciprocates with New Hampshire, North Dakota, Idaho, Oregon, Vermont, and Wyoming at the journeyperson level.[15] Colorado maintains a journeyperson alliance with Alaska, Arkansas, the Dakotas, Idaho, Iowa, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Utah, and Wyoming.[16]
Electricians use a range of hand and power tools and instruments.

Some of the more common tools are:
In addition to the workplace hazards generally faced by industrial workers, electricians are also particularly exposed to injury by electricity. An electrician may experience electric shock due to direct contact with energized circuit conductors or due to stray voltage caused by faults in a system. An electric arc exposes eyes and skin to hazardous amounts of heat and light. Faulty switchgear may cause an arc flash incident with a resultant blast. Electricians are trained to work safely and take many measures to minimize the danger of injury. Lockout and tagout procedures are used to make sure that circuits are proven to be de-energized before work is done. Limits of approach to energized equipment protect against arc flash exposure; specially designed flash-resistant clothing provides additional protection; grounding (earthing) clamps and chains are used on line conductors to provide a visible assurance that a conductor is de-energized. Personal protective equipment provides electrical insulation as well as protection from mechanical impact; gloves have insulating rubber liners, and work boots and hard hats are specially rated to provide protection from shock. If a system cannot be de-energized, insulated tools are used; even high-voltage transmission lines can be repaired while energized, when necessary.[17]
Electrical workers, which includes electricians, accounted for 34% of total electrocutions of construction trades workers in the United States between 1992 and 2003.[18]

Working conditions for electricians vary by specialization. Generally an electrician's work is physically demanding such as climbing ladders and lifting tools and supplies. Occasionally an electrician must work in a cramped space or on scaffolding, and may frequently be bending, squatting or kneeling, to make connections in awkward locations. Construction electricians may spend much of their days in outdoor or semi-outdoor loud and dirty work sites. Industrial electricians may be exposed to the heat, dust, and noise of an industrial plant. Power systems electricians may be called to work in all kinds of adverse weather to make emergency repairs.
Some electricians are union members and work under their union's policies.
Electricians can choose to be represented by the Electrical Trade Union (ETU). Electrical Contractors can be represented by the National Electrical & Communications Association or Master Electricians Australia.
Some electricians are union members. Some examples of electricians' unions include the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, Canadian Union of Public Employees, and the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers provides its own apprenticeships through its National Joint Apprenticeship and Training Committee and the National Electrical Contractors Association. Many merit shop training and apprenticeship programs also exist, including those offered by such as trade associations as Associated Builders and Contractors and Independent Electrical Contractors. These organizations provide comprehensive training, in accordance with U.S. Department of Labor regulations.
In the United Kingdom, electricians are represented by several unions including Unite the Union
In the Republic of Ireland there are two self-regulation/self certification bodies RECI Register of Electrical Contractors of Ireland and ECSSA.
An auto electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of motor vehicles. Auto electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical components. Auto electricians specialize in cars and commercial vehicles. The auto electrical trade is generally more difficult than the electrical trade due to the confined spaces, engineering complexity of modern automotive electrical systems, and working conditions (often roadside breakdowns or on construction sites, mines, quarries to repair machinery etc.) Also the presence of high-current DC electricity makes injury from burns and arc-flash injury possible.
|
|
The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the English-speaking world and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (March 2025)
|

|
|
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
|
Occupation type
|
Vocational |
|
Activity sectors
|
Maintenance, Electrical Grid |
| Description | |
|
Education required
|
Apprenticeship |
|
Fields of
employment |
Construction |
|
Related jobs
|
Lineperson |
An electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical infrastructure.[1] Electricians may also specialize in wiring ships, airplanes, and other mobile platforms, as well as data and cable lines.
Electricians were originally people who demonstrated or studied the principles of electricity, often electrostatic generators of one form or another.[2]
In the United States, electricians are divided into two primary categories: lineperson, who work on electric utility company distribution systems at higher voltages, and wiremen, who work with the lower voltages utilized inside buildings. Wiremen are generally trained in one of five primary specialties: commercial, residential, light industrial, industrial, and low-voltage wiring, more commonly known as Voice-Data-Video, or VDV. Other sub-specialties such as control wiring and fire-alarm may be performed by specialists trained in the devices being installed, or by inside wiremen.
Electricians are trained to one of three levels: Apprentice, Journeyperson, and Master Electrician. In the US and Canada, apprentices work and receive a reduced compensation while learning their trade. They generally take several hundred hours of classroom instruction and are contracted to follow apprenticeship standards for a period of between three and six years, during which time they are paid as a percentage of the Journeyperson's pay. Journeymen are electricians who have completed their Apprenticeship and who have been found by the local, State, or National licensing body to be competent in the electrical trade. Master Electricians have performed well in the trade for a period of time, often seven to ten years, and have passed an exam to demonstrate superior knowledge of the National Electrical Code, or NEC.
Service electricians are tasked to respond to requests for isolated repairs and upgrades. They have skills troubleshooting wiring problems, installing wiring in existing buildings, and making repairs. Construction electricians primarily focus on larger projects, such as installing all new electrical system for an entire building, or upgrading an entire floor of an office building as part of a remodeling process. Other specialty areas are marine electricians, research electricians and hospital electricians. "Electrician" is also used as the name of a role in stagecraft, where electricians are tasked primarily with hanging, focusing, and operating stage lighting. In this context, the Master Electrician is the show's chief electrician. Although theater electricians routinely perform electrical work on stage lighting instruments and equipment, they are not part of the electrical trade and have a different set of skills and qualifications from the electricians that work on building wiring.
In the film industry and on a television crew the head electrician is referred to as a Gaffer.
Electrical contractors are businesses that employ electricians to design, install, and maintain electrical systems. Contractors are responsible for generating bids for new jobs, hiring tradespeople for the job, providing material to electricians in a timely manner, and communicating with architects, electrical and building engineers, and the customer to plan and complete the finished product.


Many jurisdictions have regulatory restrictions concerning electrical work for safety reasons due to the many hazards of working with electricity. Such requirements may be testing, registration or licensing. Licensing requirements vary between jurisdictions.
An electrician's license entitles the holder to carry out all types of electrical installation work in Australia without supervision. However, to contract, or offer to contract, to carry out electrical installation work, a licensed electrician must also be registered as an electrical contractor. Under Australian law, electrical work that involves fixed wiring is strictly regulated and must almost always be performed by a licensed electrician or electrical contractor.[3] A local electrician can handle a range of work including air conditioning, light fittings and installation, safety switches, smoke alarm installation, inspection and certification and testing and tagging of electrical appliances.
To provide data, structured cabling systems, home automation & theatre, LAN, WAN and VPN data solutions or phone points, an installer must be licensed as a Telecommunications Cable Provider under a scheme controlled by Australian Communications and Media Authority[4]
Electrical licensing in Australia is regulated by the individual states. In Western Australia, the Department of Commerce tracks licensee's and allows the public to search for individually named/licensed Electricians.[5]
Currently in Victoria the apprenticeship lasts for four years, during three of those years the apprentice attends trade school in either a block release of one week each month or one day each week. At the end of the apprenticeship the apprentice is required to pass three examinations, one of which is theory based with the other two practically based. Upon successful completion of these exams, providing all other components of the apprenticeship are satisfactory, the apprentice is granted an A Class licence on application to Energy Safe Victoria (ESV).
An A Class electrician may perform work unsupervised but is unable to work for profit or gain without having the further qualifications necessary to become a Registered Electrical Contractor (REC) or being in the employment of a person holding REC status. However, some exemptions do exist.[6]
In most cases a certificate of electrical safety must be submitted to the relevant body after any electrical works are performed.
Safety equipment used and worn by electricians in Australia (including insulated rubber gloves and mats) needs to be tested regularly to ensure it is still protecting the worker. Because of the high risk involved in this trade, this testing needs to be performed regularly and regulations vary according to state. Industry best practice is the Queensland Electrical Safety Act 2002, and requires six-monthly testing.

Training of electricians follows an apprenticeship model, taking four or five years to progress to fully qualified journeyperson level.[7] Typical apprenticeship programs consists of 80-90% hands-on work under the supervision of journeymen and 10-20% classroom training.[8] Training and licensing of electricians is regulated by each province, however professional licenses are valid throughout Canada under Agreement on Internal Trade. An endorsement under the Red Seal Program provides additional competency assurance to industry standards.[9] In order for individuals to become a licensed electricians, they need to have 9000 hours of practical, on the job training. They also need to attend school for 4 terms and pass a provincial exam. This training enables them to become journeyperson electricians. Furthermore, in British Columbia, an individual can go a step beyond that and become a "FSR", or field safety representative. This credential gives the ability to become a licensed electrical contractor and to pull permits. Notwithstanding this, some Canadian provinces only grant "permit pulling privileges" to current Master Electricians, that is, a journeyperson who has been engaged in the industry for three years and has passed the Master's examination (i.e. Alberta). The various levels of field safety representatives are A, B and C. The only difference between each class is that they are able to do increasingly higher voltage and current work.
The two qualification awarding organisations are City and Guilds and EAL. Electrical competence is required at Level 3 to practice as a 'qualified electrician' in the UK. Once qualified and demonstrating the required level of competence an Electrician can apply to register for a Joint Industry Board Electrotechnical Certification Scheme card in order to work on building sites or other controlled areas.
Although partly covered during Level 3 training, more in depth knowledge and qualifications can be obtained covering subjects such as Design and Verification or Testing and Inspection among others. These additional qualifications can be listed on the reverse of the JIB card. Beyond this level is additional training and qualifications such as EV charger installations or training and working in specialist areas such as street furniture or within industry.
The Electricity at Work Regulations are a statutory document that covers the use and proper maintenance of electrical equipment and installations within businesses and other organisations such as charities. Parts of the Building Regulations cover the legal requirements of the installation of electrical technical equipment with Part P outlining most of the regulations covering dwellings
Information regarding design, selection, installation and testing of electrical structures is provided in the non-statutory publication 'Requirements for Electrical Installations, IET Wiring Regulations, Eighteenth Edition, BS 7671:2018' otherwise known as the Wiring Regulations or 'Regs'. Usual amendments are published on an ad hoc bases when minor changes occur. The first major update of the 18th Edition were published during February 2020 mainly covering the section covering Electric vehicles charger installations although an addendum was published during December 2019 correcting some minor mistakes and adding some small changes. The IET also publish a series of 'Guidance Notes' in book form that provide further in-depth knowledge.
With the exception of the work covered by Part P of the Building Regulations, such as installing consumer units, new circuits or work in bathrooms, there are no laws that prevent anyone from carrying out some basic electrical work in the UK.
In British English, an electrician is colloquially known as a "spark".[10]

The United States does not offer nationwide licensing and electrical licenses are issued by individual states. There are variations in licensing requirements, however, all states recognize three basic skill categories: level electricians. Journeyperson electricians can work unsupervised provided that they work according to a master's direction. Generally, states do not offer journeyperson permits, and journeyperson electricians and other apprentices can only work under permits issued to a master electrician. Apprentices may not work without direct supervision.[11]
Before electricians can work unsupervised, they are usually required to serve an apprenticeship lasting three to five years under the general supervision of a master electrician and usually the direct supervision of a journeyperson electrician.[11] Schooling in electrical theory and electrical building codes is required to complete the apprenticeship program. Many apprenticeship programs provide a salary to the apprentice during training. A journeyperson electrician is a classification of licensing granted to those who have met the experience requirements for on the job training (usually 4,000 to 6,000 hours) and classroom hours (about 144 hours). Requirements include completion of two to six years of apprenticeship training and passing a licensing exam.[12]
An electrician's license is valid for work in the state where the license was issued. In addition, many states recognize licenses from other states, sometimes called interstate reciprocity participation, although there can be conditions imposed. For example, California reciprocates with Arizona, Nevada, and Utah on the condition that licenses are in good standing and have been held at the other state for five years.[13] Nevada reciprocates with Arizona, California, and Utah.[14] Maine reciprocates with New Hampshire and Vermont at the master level, and the state reciprocates with New Hampshire, North Dakota, Idaho, Oregon, Vermont, and Wyoming at the journeyperson level.[15] Colorado maintains a journeyperson alliance with Alaska, Arkansas, the Dakotas, Idaho, Iowa, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Utah, and Wyoming.[16]
Electricians use a range of hand and power tools and instruments.

Some of the more common tools are:
In addition to the workplace hazards generally faced by industrial workers, electricians are also particularly exposed to injury by electricity. An electrician may experience electric shock due to direct contact with energized circuit conductors or due to stray voltage caused by faults in a system. An electric arc exposes eyes and skin to hazardous amounts of heat and light. Faulty switchgear may cause an arc flash incident with a resultant blast. Electricians are trained to work safely and take many measures to minimize the danger of injury. Lockout and tagout procedures are used to make sure that circuits are proven to be de-energized before work is done. Limits of approach to energized equipment protect against arc flash exposure; specially designed flash-resistant clothing provides additional protection; grounding (earthing) clamps and chains are used on line conductors to provide a visible assurance that a conductor is de-energized. Personal protective equipment provides electrical insulation as well as protection from mechanical impact; gloves have insulating rubber liners, and work boots and hard hats are specially rated to provide protection from shock. If a system cannot be de-energized, insulated tools are used; even high-voltage transmission lines can be repaired while energized, when necessary.[17]
Electrical workers, which includes electricians, accounted for 34% of total electrocutions of construction trades workers in the United States between 1992 and 2003.[18]

Working conditions for electricians vary by specialization. Generally an electrician's work is physically demanding such as climbing ladders and lifting tools and supplies. Occasionally an electrician must work in a cramped space or on scaffolding, and may frequently be bending, squatting or kneeling, to make connections in awkward locations. Construction electricians may spend much of their days in outdoor or semi-outdoor loud and dirty work sites. Industrial electricians may be exposed to the heat, dust, and noise of an industrial plant. Power systems electricians may be called to work in all kinds of adverse weather to make emergency repairs.
Some electricians are union members and work under their union's policies.
Electricians can choose to be represented by the Electrical Trade Union (ETU). Electrical Contractors can be represented by the National Electrical & Communications Association or Master Electricians Australia.
Some electricians are union members. Some examples of electricians' unions include the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, Canadian Union of Public Employees, and the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers provides its own apprenticeships through its National Joint Apprenticeship and Training Committee and the National Electrical Contractors Association. Many merit shop training and apprenticeship programs also exist, including those offered by such as trade associations as Associated Builders and Contractors and Independent Electrical Contractors. These organizations provide comprehensive training, in accordance with U.S. Department of Labor regulations.
In the United Kingdom, electricians are represented by several unions including Unite the Union
In the Republic of Ireland there are two self-regulation/self certification bodies RECI Register of Electrical Contractors of Ireland and ECSSA.
An auto electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of motor vehicles. Auto electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical components. Auto electricians specialize in cars and commercial vehicles. The auto electrical trade is generally more difficult than the electrical trade due to the confined spaces, engineering complexity of modern automotive electrical systems, and working conditions (often roadside breakdowns or on construction sites, mines, quarries to repair machinery etc.) Also the presence of high-current DC electricity makes injury from burns and arc-flash injury possible.
Yes, you'll find financing options or payment plans available for larger electrical projects. They're designed to make it easier for you to manage the cost of significant updates or installations in your home.
You're wondering about the qualifications or certifications that electricians need to stay current with electrical codes and practices. They typically hold licenses and undergo continuous training to ensure they're up to date with the latest standards.
Yes, Star Victory Electric LLC offers educational resources and workshops for homeowners. You'll learn basic electrical safety and maintenance, helping you manage minor issues and understand when it's crucial to call in the professionals.