

Fireproof doors are vital for building safety, acting as barriers against fire and smoke, providing crucial time for evacuation, and protecting property. Learn about their construction, regulatory standards, and innovations in fire door technology to enhance safety and potentially lower insurance premiums. FireResist - specializing in certified Fireproof Doors , windows and walls. We design, manufacture, and install systems that meet safety standards. Fireproof doors are a critical component in modern building safety. They serve as barriers against the spread of fire and smoke, providing occupants with valuable time to evacuate safely. These doors are not just about compliance; they are about saving lives and protecting property. In any building, the risk of fire is a serious concern. Fireproof doors help mitigate this risk by containing fires to specific areas, reducing potential damage. They are engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke. Understanding the importance of fireproof doors is essential for anyone involved in building design, construction, or management. This post will delve into various aspects of fireproof doors, from their construction materials to their role in emergency plans. We will also explore the regulatory standards that govern their use and the latest innovations in fire door technology.
Fireproof doors are vital for building safety. They act as a barrier to fire and smoke, slowing their spread. This containment is crucial in preventing a fire from engulfing an entire building. By compartmentalizing the fire, these doors provide occupants with more time to evacuate safely. They also protect escape routes, ensuring that stairwells and corridors remain passable during an emergency. The design of fireproof doors focuses on resisting high temperatures. They are tested to withstand fire for a specified period, usually ranging from 30 minutes to several hours. This resistance is critical in high-risk areas such as kitchens, boiler rooms, and storage areas containing flammable materials. Fireproof doors also play a role in protecting property. By containing the fire, they limit damage to specific areas, reducing repair costs. This containment can be the difference between a minor incident and a catastrophic loss. In addition to their physical properties, fireproof doors are often equipped with automatic closing mechanisms. Fire door maintenance Romford These ensure that the doors close securely in the event of a fire, even if left open. This feature is essential in maintaining the integrity of fire compartments.
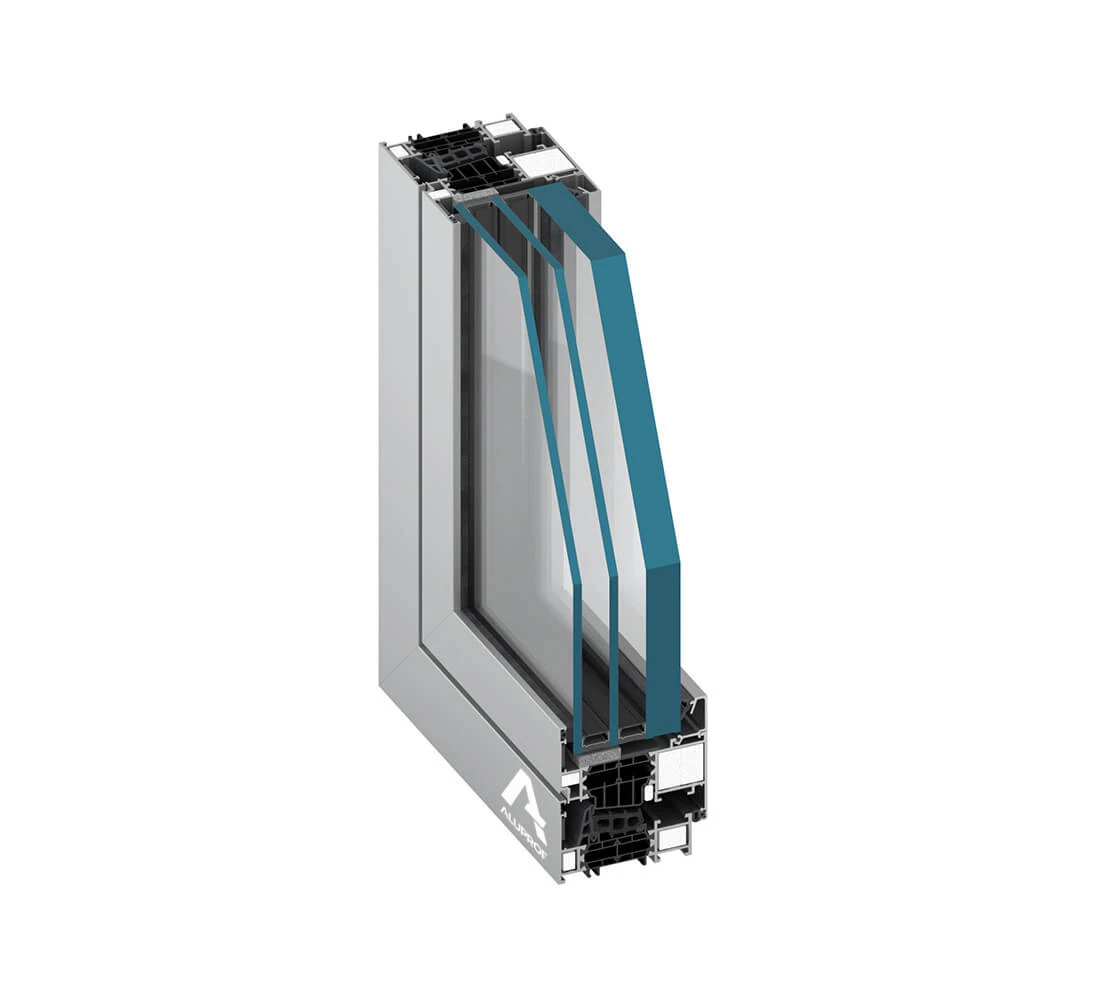
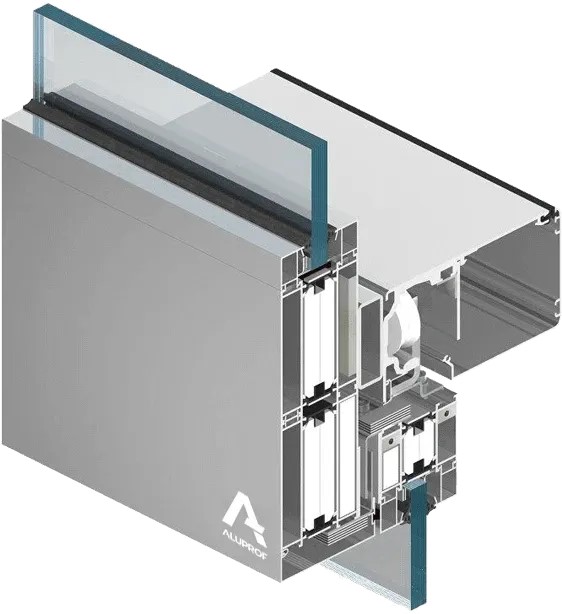
Fire-resistant doors are constructed from materials designed to withstand high temperatures. Steel is a common choice due to its strength and durability. It provides excellent resistance to fire and is often used in commercial and industrial settings. Another popular material is solid timber. When treated with fire-retardant chemicals, timber doors can offer significant fire resistance. They are often used in residential buildings where aesthetics are a consideration. Glass is also used in fire-resistant doors, but it must be specially treated. Fire-rated glass can withstand high temperatures and prevent the passage of flames and smoke. It is often used in combination with steel or timber frames to provide both safety and visibility. Composite materials are increasingly popular in fire door construction. These materials combine the benefits of different substances, offering enhanced fire resistance and durability. They are often lighter than traditional materials, making them easier to install and maintain. Intumescent seals are another critical component. These seals expand when exposed to heat, filling gaps around the door to prevent the passage of smoke and flames. They are an essential feature of any fire-resistant door, ensuring that it performs effectively in an emergency.
The fire rating system for doors is a crucial aspect of building safety. It indicates how long a door can withstand fire and heat. Ratings are typically expressed in minutes, such as FD30 or FD60, representing 30 or 60 minutes of fire resistance. These ratings are determined through rigorous testing. Doors are exposed to high temperatures in controlled conditions to assess their performance. The tests evaluate the door's ability to contain fire and smoke, as well as its structural integrity. Fire ratings are essential for compliance with building codes and regulations. They ensure that doors meet the necessary safety standards for their intended use. Different areas of a building may require doors with varying fire ratings, depending on the level of risk. Understanding fire ratings helps in selecting the right door for each application. For example, a high-risk area like a kitchen may require a door with a higher fire rating than a standard office. It's important to note that fire ratings apply to the entire door assembly, including the frame, hardware, and seals. All components must work together to achieve the desired level of protection.
Proper installation of fireproof doors is critical for their effectiveness. The process begins with selecting the right door for the specific application. Consider the fire rating, materials, and any additional features required for the location. Once the door is selected, ensure that the frame is correctly installed. It must be securely anchored to the surrounding structure to maintain its integrity during a fire. Any gaps between the frame and the wall should be filled with fire-resistant materials. The door itself must be hung correctly. It should open and close smoothly, with no obstructions. The hinges and hardware should be fire-rated and installed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Intumescent seals are a vital component of fireproof doors. They must be fitted correctly to ensure they expand and seal gaps in the event of a fire. Check that the seals are in good condition and replace them if necessary. Finally, test the door's automatic closing mechanism. It should close securely without assistance. Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure the door remains in good working order.
Fire doors are a critical element of emergency evacuation plans. They help contain fires, allowing occupants more time to evacuate safely. By protecting escape routes, fire doors ensure that stairwells and corridors remain passable during an emergency. In an evacuation plan, fire doors are strategically placed to compartmentalize the building. This compartmentalization prevents the fire from spreading rapidly, giving occupants more time to reach safety. Fire doors also play a role in directing the flow of people during an evacuation. By closing off certain areas, they guide occupants towards designated exits. This guidance is crucial in preventing confusion and ensuring a smooth evacuation. It's important to include fire doors in regular evacuation drills. Timber fire doors This practice ensures that occupants are familiar with their location and function. It also helps identify any potential issues with the doors, such as faulty closing mechanisms or damaged seals. In summary, fire doors are an essential component of any emergency evacuation plan. They provide vital protection and guidance, helping to ensure the safety of building occupants.
Regular maintenance and inspection of fire-resistant doors are essential for their effectiveness. Begin by checking the door's overall condition. Look for any signs of damage, such as dents or warping, which could compromise its integrity. Inspect the door's hardware, including hinges, locks, and handles. Ensure they are in good working order and replace any damaged components. Fire-rated hardware is essential for maintaining the door's fire resistance. Examine the intumescent seals around the door. These seals should be intact and free from damage. Replace any seals that are worn or missing to ensure they function correctly in a fire.
Fireproof doors differ significantly from standard doors in terms of construction and function. They are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke. This capability is crucial for building safety and compliance with regulations. Standard doors, on the other hand, are not built to resist fire. They may be made from materials that burn easily, such as untreated wood or lightweight composites. In a fire, these doors can quickly become a hazard, allowing flames and smoke to spread. Fireproof doors are constructed from fire-resistant materials like steel, treated timber, or composite materials. They often include intumescent seals that expand in heat, sealing gaps and preventing smoke passage. In terms of cost, fireproof doors are generally more expensive than standard doors. However, their benefits in terms of safety and compliance often outweigh the initial investment. In summary, fireproof doors offer superior protection compared to standard doors. They are an essential component of any building's fire safety strategy, providing critical time for evacuation and reducing potential damage.
Regulatory standards for fire doors in commercial buildings are stringent. They ensure that doors provide adequate protection in the event of a fire. Compliance with these standards is essential for building safety and legal requirements. Fire doors must meet specific fire ratings, indicating their ability to withstand fire for a set period. These ratings are determined through rigorous testing and are a key component of building codes. In addition to fire ratings, fire doors must be installed according to specific guidelines. This includes using fire-rated hardware and ensuring that the door closes automatically in a fire. Certified fire doors Regular inspections are required to ensure that fire doors remain in good working order. Any damage or wear must be addressed promptly to maintain compliance. Failure to comply with regulatory standards can result in significant penalties. It can also compromise the safety of building occupants and increase the risk of fire-related damage. In conclusion, understanding and adhering to regulatory standards for fire doors is crucial for commercial building safety. These standards ensure that doors provide the necessary protection in the event of a fire.
Fire doors can have a significant impact on insurance premiums. By enhancing building safety, they reduce the risk of fire-related damage. This reduction in risk can lead to lower insurance costs. Insurance companies often consider the presence of fire doors when assessing a building's risk profile. Buildings with properly installed and maintained fire doors are seen as less risky, resulting in more favorable premiums. In addition to reducing premiums, fire doors can also affect coverage terms. Fire protection Romford Some insurers may require fire doors as a condition of coverage, particularly in high-risk areas. It's important to note that the quality and condition of fire doors are crucial. Insurers may require regular inspections and maintenance to ensure that the doors remain effective. In summary, fire doors play a vital role in managing insurance costs. They enhance building safety, reduce risk, and can lead to more favorable insurance terms.
Innovations in fire door technology continue to enhance building safety. New materials and designs offer improved fire resistance and durability. These advancements ensure that fire doors remain effective in protecting occupants and property. One area of innovation is the use of composite materials. These materials combine the benefits of different substances, offering enhanced fire resistance and strength. Fire safety equipment They are also lighter than traditional materials, making them easier to install and maintain. Smart technology is also making its way into fire doors. Automated systems can monitor the status of fire doors, ensuring they are closed and functioning correctly. These systems can alert building managers to any issues, allowing for prompt maintenance. Fire-rated glass is another area of advancement. New treatments and coatings offer improved fire resistance while maintaining visibility. This innovation is particularly useful in areas where visibility is important, such as corridors and stairwells. In conclusion, innovations in fire door technology continue to improve building safety. These advancements ensure that fire doors remain a critical component of any fire safety strategy.
Fireproof doors are essential for building safety. They protect lives and property by containing fires and smoke. Understanding their importance is crucial for anyone involved in building management or design. From their construction materials to their role in emergency plans, fireproof doors are a vital component of any safety strategy. Regular maintenance and compliance with regulatory standards ensure their effectiveness. Innovations in technology continue to enhance their performance, offering improved protection. Fireproof doors also impact insurance premiums, reducing risk and potentially lowering costs.
Fire Resist
Share
Hours: Open ⋅ Closes 6 pm
https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/p/AF1QipNUAsReVBecS7relwQPYnWJo5BluU4b1pB9fbW2=s680-w680-h510
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Entity | Description | Link |
| Fireproof doors | Doors designed to resist fire and prevent the spread of flames and smoke between compartments of a building. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire doors Romford | Fire-resistant doors installed in properties within Romford, England. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| FD30 fire doors | Fire doors rated to resist fire for 30 minutes under British Standard BS 476. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| FD60 fire doors | Fire doors rated to resist fire for 60 minutes, offering enhanced fire protection. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Certified fire doors | Fire doors that have passed official testing and certification according to regulatory fire safety standards. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire door installation Romford | Installation services for fire-resistant doors in residential or commercial properties in Romford. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Commercial fire doors | Fire doors specifically designed for use in commercial buildings to contain fire and smoke. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Residential fire doors | Fire-rated doors used in homes and multi-unit residential buildings for safety and compliance. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire-rated doors Romford | Doors installed in Romford that meet official fire-resistance standards. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Internal fire doors | Fire doors located inside buildings to prevent fire from spreading between rooms or corridors. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire door regulations UK | Legal requirements in the United Kingdom for the manufacture, installation, and maintenance of fire doors. | |
| BS 476 fire door standard | A British Standard specification that tests the fire resistance of building materials including doors. | BS 476 – Wikipedia |
| Fire safety compliance Romford | Adhering to fire safety codes and laws specific to Romford and the wider UK. | |
| Fire door suppliers Romford | Suppliers and retailers of certified fire doors located in Romford. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Steel fire doors | Fire doors made primarily from steel, offering high durability and fire resistance. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Timber fire doors | Fire doors made from specially treated timber to resist fire for designated periods. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire door certification | The process of officially verifying a fire door's compliance with fire safety standards. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire door maintenance Romford | Regular inspection and maintenance of fire doors in Romford to ensure continued compliance and function. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Building regulations Part B | UK building code section that outlines fire safety requirements, including fire doors. | |
| Fire door inspection services | Professional services that assess and report on the safety and effectiveness of installed fire doors. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Local fire door fitters Romford | Skilled tradespeople or companies based in Romford who specialize in fitting fire doors. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Fire resistance rating | A metric indicating how long a passive fire protection system can withstand fire exposure. | |
| Fire safety products Romford | A range of fire prevention and safety equipment available in Romford, including fire doors. | Fire protection – Wikipedia |
| UK fire safety standards | National fire safety codes and standards governing the construction and operation of buildings in the UK. | |
| Fire protection Romford | Measures and systems in place in Romford to prevent, contain, and suppress fires. | Fire protection – Wikipedia |
| Fire safety equipment | Equipment used to detect, prevent, and control fires, such as extinguishers, alarms, and fire doors. | Fire protection – Wikipedia |
| Passive fire protection | Fire safety features integrated into a building’s structure, such as fire doors, walls, and floors. | |
| Fire door hardware | Components used in fire door assemblies such as hinges, closers, latches, and intumescent strips. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Self-closing fire doors | Fire doors with automatic closing mechanisms to ensure doors shut when not in use or in an emergency. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
| Smoke seals fire doors | Sealing systems fitted to fire doors to block smoke from passing through gaps during a fire. | Fire door – Wikipedia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fire Resist
Share
Hours: Open ⋅ Closes 6 pm
https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/p/AF1QipNUAsReVBecS7relwQPYnWJo5BluU4b1pB9fbW2=s680-w680-h510
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Driving map directions
22 languages
Tools
Appearance hide
Text
Width
Color (beta)
Coordinates: 51.5768°N 0.1801°E
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Romford is a large town in east London, England.[2] Part of the London Borough of Havering, the town is one of the major metropolitan centres of Greater London identified in the London Plan.[3]
The Romford post town covers all of the former municipal borough and extends over a much wider area, including parts of Barking and Dagenham, Thurrock, and Epping Forest.[4]
Historically part of the ancient parish of Hornchurch in the Becontree hundred of Essex, Romford has been a market town since 1247. It formed the administrative centre of the liberty of Havering until that liberty was dissolved in 1892, and became a civil parish of its own in 1849.[5][6] Good road links to London and the opening of the railway station in 1839 were key to the development of the town.[5] The economic history of Romford is characterised by a shift from agriculture to light industry and then to retail and commerce.[5]
As part of the suburban growth of London throughout the 20th century, Romford significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming a municipal borough in 1937. In 1965, following reform of local government in London, it merged with the Hornchurch Urban District to form the London Borough of Havering, and was incorporated into Greater London.[7][8][9] Today, it is one of the largest commercial, retail, entertainment and leisure districts in London and has a well-developed night-time economy.[10][11] The population of Romford, as of the 2011 census, was 122,854.[12]
History[edit]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Toponymy[edit]
Romford is first recorded in 1177 as Romfort, which is formed from Old English 'rūm' and 'ford' and means "the wide or spacious ford".[14] The naming of the River Rom is a local 'back-formation' from the name of the town; and the river is elsewhere known as the Beam. The ford most likely existed on the main London to Colchester road where it crossed that river.[14]
Economic development[edit]
Romford in 1851
The town developed in the Middle Ages on the main road to London and the regionally significant Romford Market was established in 1247.[5] The original site of the town was to the south, in an area still known as Oldchurch. It was moved northwards to the present site in the later medieval period to avoid the frequent flooding of the River Rom. The first building on the new site was the 1410 Chapel of St Edward[15] (since replaced by the 1850 Parish Church of St Edward the Confessor. The early history of Romford and the immediate area is agricultural and it is recorded as being the location of a number of mills used to grind corn.[5] The area was a focus of the leather industry from the 15th to the early 19th centuries and there is record of a wide range of industries such as cloth making, weaving, charcoal burning, metal working and brewing.[5] Communications played an important part in its development; the main road to London was maintained by the Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust from 1721 and Romford became a coaching town in the 18th century.[16]
Several failed attempts were made in the early 19th century to connect the town to the Thames via a Romford Canal.[17] It was initially intended to terminate at a basin near to the Star Brewery, to transport agricultural products to London and, eventually, to serve growing industrial sites in Romford. A later proposal included an extension to Collier Row, whereby timber from Hainault Forest could be transported to the Thames for use in the Royal Dockyards. Only two miles of canal were constructed and the canal company were unable to reach the town.[18]
The development of the town was accelerated by the opening of the railway station in 1839 which stimulated the local economy and was key to the development of the Star Brewery. Initially Eastern Counties Railway services operated between Mile End and Romford, with extensions to Brentwood and to Shoreditch in 1840. A second station was opened on South Street in 1892 by the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway on the line to Upminster and Grays, giving Romford a rail connection to Tilbury Docks. The two stations were combined into one in 1934.[16] Light industry slowly developed, reaching a peak in the 1970s with a number of factories on the edge of town, such as the Roneo Vickers office machinery company, Colvern manufacturers of wireless components, May's Sheet Metal Works and brush manufacturers Betterware.[5] Suburban expansion increased the population and reinforced Romford's position as a significant regional town centre. The Liberty Shopping Centre was constructed in the 1960s, and has been modernised and supplemented with further shopping centres throughout the town, including The Mall, opened in 1990 (as 'Liberty 2'); and The Brewery, opened in 2000 on the site of the old Star Brewery.[19]
Local government[edit]
Romford formed a chapelry in the large ancient parish of Hornchurch in the Becontree hundred of Essex; as well as the town it included the wards of Collier Row, Harold Wood, and Noak Hill.[20] Through ancient custom the area enjoyed special status and a charter in 1465 removed the parish from the Becontree hundred and the county of Essex and it instead formed the independent liberty of Havering governed from a court house in the market place.[6] Over time the vestry of Romford chapelry absorbed the local powers that would usually be held by the parish authorities in Hornchurch[20] and in 1849 Romford became a separate parish within the liberty.[21] Improvement commissioners were set up in 1819 for paving, lighting, watching, and cleansing of the marketplace and main streets.[20] As the town grew this arrangement became ineffective at controlling sanitation and in 1851 a local board of health was set up for the parish; although its area was reduced in 1855 to cover only the town ward.[20] The remainder of the parish became part of the Romford rural sanitary district in 1875. These changes and the introduction of the Romford Poor Law Union in 1836[20] eroded the powers of the liberty and it was finally abolished in 1892 and reincorporated into Essex.[6]
The Local Government Act 1894 reformed local government and created the Romford Urban District and Romford Rural District to replace the local board and sanitary district; following which the Romford parish was split into Romford Urban and Romford Rural along the lines of the urban district.[20] In 1900 the parish was recombined and the urban district expanded to cover all of the former area of the historic chapelry, except for Noak Hill which remained in the rural district and had become a parish in its own right in 1895.[20] The enlarged urban district formed part of the London Traffic Area from 1924 and the London Passenger Transport Area from 1933.[22] The suburban expansion of London caused an increase in population during the 1930s[7] and the urban district was expanded further in 1934, taking in the parishes of Havering-atte-Bower and Noak Hill.[8] It was incorporated as the Municipal Borough of Romford in 1937.[8] In 1965 the municipal borough was abolished and its former area was combined with that of Hornchurch Urban District; it was again removed from Essex and since then has formed the northern part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.[23] For elections to the Greater London Council, Romford was part of the Havering electoral division until 1973 and then the Romford electoral division until 1986.
Suburban expansion[edit]
Romford Urban District (1) absorbed Havering-atte-Bower (2) and Noak Hill (3) in 1934[8]
There was early expansion in the 1840s when 200 cottages were built in the area formerly occupied by an army barracks; it was known as New Romford.[16] To acknowledge the military connection, when in 1961 these were in turn replaced with new housing the name Waterloo Road Estate was applied.[24] To the east of the market place from 1850 middle class suburban housing was constructed with a much larger area of 200 acres (80 hectares) built-over to the south of the railway from 1851 and by 1861 the population had grown to 3790.[25] Through a gradual process of selling off former manors, houses were built radiating from the town in all directions for about a mile, and further significant growth occurred between 1910 and 1911 with the construction of Romford Garden Suburb, which included Raphael Park and Gidea Park railway station.[16] Large sections of land to the north of the town at Collier Row were developed in the interwar period and after World War II, the London County Council built the Harold Hill estate to the north east from 1948 to 1958.[16]
The right to supply electricity to the town was secured by the County of London Electricity Supply Company in 1913. Initially power was generated within the Star Brewery site, with the supply switching to Barking Power Station in 1925.[20] Gas supply began in 1825 with gas works of 25 acres (10 ha) constructed by 1938.[20] Following the Telegraph Act 1899 Romford became part of the Post Office London telephone area[26] and the Romford exchange was recorded as having 240 subscribers in 1916.[27] The town water supply initially came from the Havering Well, and 1859 a new public well and pump was built at the east end of the market.[20] The South Essex Waterworks Company started installing mains water supply in 1863 and had offices in South Street. By 1905 its supply was serving Ilford, Collier Row, Ardleigh Green, Brentwood, and Hornchurch. Sewage works were installed by the local board at Oldchurch in 1862, with further works built in Hornchurch in 1869.[20]
Romford Cemetery[edit]
Romford Cemetery entrance
Crow Lane or Romford Cemetery was established by the Romford Burial Board in 1871 when space ran out in the parochial cemetery. It was taken over by Romford Urban District Council in 1900 and is now run by the South Essex Crematorium. It is partially enclosed by 19th-century railings, with ragstone gate-piers and two ragstone chapels joined by a gothic porte-cochère. It contains utilitarian monuments, with older graves near the chapels. The trees in the cemetery include holly, cedar and flowering cherry, and rows of common lime and horse chestnut.[28] The cemetery contains the war graves of 118 identified Commonwealth service personnel of the First and Second World Wars.[29]
Governance[edit]
Romford constituency in Greater London
The Romford UK Parliament constituency consists of the Havering wards of Brooklands, Havering Park, Hylands, Mawneys, Pettits, Romford Town, and Squirrel's Heath.
The MP since 2001 is Andrew Rosindell of the Conservative Party, a native of the town. Romford forms part of the Havering and Redbridge London Assembly constituency.
Each ward elects three councillors to Havering London Borough Council. As of the 2018 council elections, all the elected councillors for the wards in Romford constituency were Conservative.[30]
Sport[edit]
Romford F.C., who currently play in the Essex Senior League, is the local football team. The London Raiders ice hockey team are based in Romford. Romford is home to the Romford and Gidea Park Rugby Football Club, which was established in 1927. In 2003, the club became one of the first in the country to have a ladies Rugby team.
Geography[edit]
Further information: Geography of London
The River Rom emerges from underground channels at Roneo Corner.
Map of Romford and its environs
15 mile radius map for Romford
The town centre is about 50 feet (15 m) above sea level on a gravel terrace rising from the River Thames.[16] The north of the town has developed on London Clay and is situated as much as 150 ft (46 m) above sea level. A continuous gentle rise in the eastern suburbs towards Gidea Park and Harold Wood peaks around 177 feet (54 m) around the Harold Court. On the northern side, Harold Hill peaks at 75 m (246 ft). The semi-rural area north of Collier Row and Harold Hill consists of many rolls of hills, with elevation peaking at the village of Havering-atte-Bower, 344 feet (105 m). The town centre is for the most part contained within a ring road formed of St Edwards Way, Mercury Gardens, Thurloe Gardens, Oldchurch Road and Waterloo Road. The market place and much of South Street and the High Street are pedestrianised.[10] The railway cuts through the town from east to west on a viaduct, with the bulk of the central Romford area to its north. The River Rom flows through the town in underground channels and joins the Thames after flowing through Hornchurch;[16] elsewhere along its course it is known as the River Beam[14] and forms part of the strategic waterways Blue Ribbon Network.[31]
Romford has formed part of the continuously built-up area of London since the 1930s[32] and is contiguous with Rush Green to the west, Collier Row to the north, Gidea Park to the east and Hornchurch to the south east. Neighbourhoods of Romford include: Collier Row, Gidea Park, Harold Hill, Harold Park, Harold Wood, Havering-atte-Bower, Rise Park and Rush Green.
Romford is located 14 mi (23 km) northeast of Charing Cross in central London; 4
+
3⁄4 mi (7.5 km) northeast of Ilford; 2
+
1⁄2 mi (4 km) north of Dagenham; 9 mi (14 km) northwest of Grays; 6 mi (10 km) south-west of Brentwood; 12 mi (19 km) west of Basildon; and 9 mi (14 km) southeast of Epping.
Climate[edit]
Climate data for Romford is taken from the nearest weather station at Greenwich, around 10 miles (16 km) southwest of the marketplace.
|
|
Demography[edit]
Further information: List of districts in Havering
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Havering committee area for Romford is defined as the wards of Romford Town and Brooklands.[40] Demographic data is produced by the Office for National Statistics for these wards. In 2001 the population of Romford Town was 13,200[38] and Brooklands was 13,024,[39] giving a total population of 26,224. In contrast, the approximate population of the area within the 2005 Romford Urban Strategy was estimated to be 36,500.[10] 71.52% in Romford Town and 70.48% in Brooklands report their religion as Christian, compared to 76.13% for Havering, 58.23% in London and 71.74% in England. 15.71% in Romford Town and 16.62% in Brooklands report having no religion, compared to 13.18% in Havering, 15.76% in London and 14.59% in England.[38][39]
In 2011, the Romford Parliament constituency was 82% White British, 5.8% Asian, 5% Other White and 4.7% Black out of a total population of 95,894. The constituency is predominantly Christian with 64% of the residents reporting that religion.[41]
Out of the wards that make up Romford overall, the highest male life expectancy was in Squirrel's Heath (80.7 years) while the highest female expectancy was in Romford Town (85.7 years). The lowest were Heaton (76.2 years) and Heaton and Gooshays (both 81.3 years) respectively.[42]
The average house price as of 2014 was £225,000 in Romford Town ward. In the Pettits ward, 87.5% of houses were owned by households; the lowest figure, and the only minority one, was Gooshays ward with 48.6%.[42]
Economy[edit]
The market place
The market place
Romford is recognised in the London Plan as one of 13 regionally significant metropolitan centres in Greater London, with a considerable catchment area.[10] The total commercial floorspace in the town was 353,258 m2 (3,802,440 sq ft) in 2002, of which 147,627 m2 (1,589,040 sq ft) was retail space and 63,357 m2 (681,970 sq ft) was offices. The retail space is growing and in 2005 consisted of 190,000 m2 (2,000,000 sq ft).[19] The retail economy is complemented by a central business district close to the railway station, where the offices of employers such as Aon are located. Employment in the town centre was categorised in 2002 as approximately 40% commercial office, 40% comparison retail, 10% hospitality, 5% public sector, 2.5% service retail and 2.5% arts and entertainment.[10] Compared to the similar east London areas of Ilford, Stratford and Barking, there is more comparison retail and commercial office employment in Romford and less public sector work.[10] The total turnover of £413,395,000 in 2002 for Romford was larger than any other comparable town centre in east London and approximately 70% came from the commercial office businesses.[10][needs update]
There is a developed night time economy, greater than in any other metropolitan centre in Greater London, with 8,360 m2 (90,000 sq ft) of cinemas, theatres and concert hall space; 9,530 m2 (102,600 sq ft) of bars and pubs; 5,510 m2 (59,300 sq ft) of cafés and restaurants; and 2,680 m2 (28,800 sq ft) of fast food and take away venues.[11] The night time economy is almost as significant as the day economy with around 12,000 visits to Romford during the day and 11,000 visits to pubs, clubs and bars at night.[10]
As of 2012, Romford has 207,025 m2 (2,228,400 sq ft) of total town centre floorspace (retail, leisure and vacant), placing it fifth in Greater London only behind the West End, Croydon, Kingston upon Thames and Stratford for "town centre vitality and viability".[43]
Transport[edit]
Further information: Transport in London and Public transport in Havering
Railway[edit]
Romford railway station
The town is served by Romford railway station; it is situated on the Great Eastern Main Line in London fare zone 6.[44] Elizabeth line trains on the line's Shenfield branch call at the station.[45]
Some Greater Anglia services to/from Southend Victoria and Colchester Town also call at the station. A branch line shuttle between Romford and Upminster (the Liberty line) is operated by London Overground.[45]
Buses[edit]
Romford is a hub of the London Buses network, with services to Canning Town, Stratford, Leytonstone and Dagenham; there are also feeder services from the large housing developments at Collier Row and Harold Hill.[46] There are night bus services to Stratford, Harold Hill and Paddington.[47] Romford town centre has a very high Public Transport Accessibility Level score of 6.[10]
As of 2009, there was a proposal that Romford will be served by a future extension of the East London Transit.[48]
Roads[edit]
The A12 trunk road passes to the north of Romford, while the A118 road from Stratford connects with it at Gallows Corner at the start of the A127 road to Southend.[49]
Culture[edit]
Welcome sign at Roneo Corner with the coat of arms and motto of Havering London Borough Council
Brookside Theatre entrance
In 2005, Havering Council's urban strategy had the stated aims of making Romford a cultural destination, whilst recognising that Hornchurch forms the main cultural hub of the borough with a large theatre and arts spaces.[10] As a former market and coaching town, Romford is well served by public houses and two that are located in the market place are listed buildings.[50] The market and adjacent streets also form a conservation area.[10][51]
Mass entertainment facilities in the town include the Brookside Theatre, Romford Greyhound Stadium, one of the few remaining dog racing tracks in London;[52] 2 multi-screen cinemas;[10] and until April 2013 Romford Ice Arena, which was home to the local Romford Raiders ice hockey team.[53][54] The Dolphin Centre was a popular swimming and leisure facility located in the town from 1982 to 1995, but the site was redeveloped into the current Axis residential tower block and Asda superstore in the mid-2000s. There is also a Romford F.C. associated with the town.[55] Romford Bowls Club is based in Lodge Farm Park. 1980s Post Punk bands Department S and Purple Hearts both have origins in Romford. The town is strongly associated with the electronic music group Underworld, who cite Romford in their hit "Born Slippy", affiliated to the movie Trainspotting.[56]
Ride the sainted rhythms on the midnight train to Romford
— Dirty Epic on dubnobasswithmyheadman, Underworld (1994)[56]
Romford's position as a focus for electronic music production was reinforced by the presence of the Strictly Underground and Suburban Base record labels, with Suburban Base developing from the Boogie Times record store.[57] According to a Billboard article in 1992, Romford-produced dance music formed part of a trend favouring suburban and provincial "bedroom" record labels over those in central London.[58] In 2013, the film Death Walks was filmed in Romford over a four-month period. The cult TV series Garth Marenghi's Darkplace was set in the fictional Darkplace Hospital, in Romford.[citation needed]
The local newspapers for the town and the borough of Havering are the Romford Recorder, Romford and Havering Post and Romford Yellow Advertiser.[citation needed]
Two radio stations are located in the area: Time 107.5[59] and Bedrock Radio (a community health and hospital radio station).[60] A proposed new community service, Radio Romford, is planned to launch in 2024.[61]
In April 2023, hoodies were banned from the town centre along with Ski masks and motorcycle helmets in an initiative by Romford Business Improvement District, backed by Havering councillors and local Metropolitan Police officers, as a measure against antisocial behaviour.[62]
Premier Cinemas, located within the Mercury Mall, has served as the venue for the Romford Film Festival since 2017, the Romford Horror Film Festival since 2020, and the East London LGBTQ+ Film Festival since 2023.[63][64][65]
19 languages
Tools
Appearance hide
Text
Width
Color (beta)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
|
|
|
Fire-resistance rated door, with wire mesh glass vision panel
Industrial grade fire door rated to hydrocarbon curve and blast resistance
Double fire door immediately after 3-hour fire test inside a 4-hour rated Durasteel wall
Double fire door after 3-hour fire test in a 4-hour Durasteel wall, during successful 45PSI (3.1 bar) hose stream test leading to a UL Listing[1]
A fire door is a door with a fire-resistance rating (sometimes referred to as a fire protection rating for closures) used as part of a passive fire protection system to reduce the spread of fire and smoke between separate compartments of a structure and to enable safe egress from a building or structure or ship.
In North American building codes, a fire door, along with fire dampers, is often referred to as a closure, which can be derated compared against the fire separation that contains it, provided that this barrier is not a firewall or an occupancy separation. In Europe, national standards for fire doors have been harmonised with the introduction of the new standard EN 16034, which refers to fire doors as fire-resisting door sets. Starting September 2016, a common CE marking procedure was available abolishing trade barriers within the European Union for these types of products.
In the UK, it is Part B of the Building Regulations that sets out the minimum requirements for the fire protection that must be implemented in all dwellings this includes the use of fire doors. All fire doors must be installed with the appropriate fire resistant fittings, such as the frame and door hardware, for it to fully comply with any fire regulations.[citation needed] The British Woodworking Federation outlines the difference between a 'Fire Doorset' and a 'Fire Door Assembly'.[2]
Components[edit]
Fire doors may be made of a combination of materials, such as:
Both the door leaf (the swinging panel of the door) and the door frame are required to meet the guidelines of the testing agency which provides the product listing. The door frame includes the fire or smoke seals, door hardware, and the structure that holds the fire door assembly in place. Together, these components form an assembly, typically called a "doorset" which holds a numerical rating, quantified in minutes or hours of resistance to a test fire. All of the components of the fire door assembly must bear a listing agencies label (with the exception of ball-bearing hinges which meet the basic build requirements of ANSI 156.2 and NFPA 80) to ensure the components have been tested to meet the fire rating requirements.
Door hardware[edit]
Door hardware includes:
Seals[edit]
Edges of a fire door usually need to have fire rated seals which can be composed of:
When intumescent seals are used in the door design, use of the correct seal is crucial in the fire rating performance the door assembly. Seals may vary in chemical composition, expansion rate, expansion volume, and/or charring characteristics.
Windows[edit]
Some fire doors are equipped with integral windows which also have a rating, or have been incorporated at the time of the door test and be subject to the overall door's product certification. Fire-resistive windows must remain intact under fire conditions and hose stream impact resistance, and can include:
Wired glass typically withstands the fire, whereas the sodium silicate liquid also acts to insulate heat transfer, due to the endothermic action of this chemical.
Fire door rating label
In the United States, wire glass must pass the requirements of 16 CFR 1201 and be "labeled" to be used in a door. Laminate and ceramic glasses are now more likely to be used, as they more readily meet the requirements of 16 CFR 2101.
Regulations[edit]
All components are required to adhere to product certification requirements that are acceptable to the local Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) by meeting the requirements of the local building code and fire code. The regulatory requirement change from country to country. For example, in Australia, the National Construction Code dictates that all fire doors must be tested to certain specifications in order to meet resistance approvals and certification.[3]
In the United Kingdom a fire resisting doorset should be subjected to either a British Standard Fire Test BS 476 Part 22 1987, or a BS/EN 1634-1 2000 test. The results are recorded by the test agency and provided in a report which detail such things as constructional details, distortion data and pressure readings. The numerical fire resistance rating that is required to be installed in a particular building is provided in the Building Regulations approved Document B, or British Standards such as the BS 5588 series (e.g., 30 minutes FD30, or FD30(S) if cold smoke resistance is also required). Classifications in use which reflect the number of minutes of fire resistance offered are FD30, FD60, FD90 and FD120.[4]
Similar technical guidance documents and building regulations are in effect in other countries.
Combustibility[edit]
Fire doors are not necessarily noncombustible. It is acceptable for portions of the door to be destroyed by combustion during exposure to fire as long as the door assembly meets the fire test criteria of limiting temperature on the non-fire side of the assembly. This is in accordance with the overall performance goal of a fire-rated door to slow fire propagation from one fire rated compartment to another for only a limited amount of time, during which automatic or manual fire fighting may be employed to limit fire spread, or occupants can exit the building. Fire doors are made from a range of different materials such as timber or steel. Despite not being fire resistant, timber is used as it has a very predictable char rate, depending on the density and the moisture content timber generally has a char rate of 0.5mm per minute for hardwood and 0.7mm per minute for softwood.[5]
Fire door failure[edit]
Fire doors are sometimes rendered unable to provide their listed fire resistance by ignorance of the intended use and associated restrictions and requirements, or by improper use. For example, fire doors are sometimes blocked open, or carpets are run through them, which would allow the fire to travel past the fire barrier in which the door is placed. The door's certification markings are displayed both on the door leaves and the fire door frames, and should not be removed or painted over during the life of the building.
Sometimes fire doors have apparently very large gaps at the foot of them, an inch or two even, allowing air movement, such as in dormitory facilities. This can lead the occupants of a building to question their status as 'real' fire doors. NFPA 80 allows a maximum door undercut of 3/4 inch, however fire doors are tested with smaller clearances in accordance with NFPA 252.[6] Corridors have a fire rating of one hour or less, and the fire doors in them are required by code to have a fire rating of 1/2 or 1/3 hour, the intent of which is mainly to restrict smoke travel.[7]
Normal operation[edit]
Fire door held open by an electromagnetic door holder
Most fire doors are designed to be kept closed at all times. Some doors are designed to stay open under normal circumstances, and close automatically in the event of a fire. Whichever method is used, the door's movement should never be impaired by a doorstop or other obstacle. The intumescent and smoke-seal bounding of fire doors should be routinely checked, as should the action of the door closer and latch.
Some fire doors are held open by an electromagnetic door holder, which is typically wired to a fire alarm system. If the power fails or the fire alarm is activated, the coil is de-energized, and the door closes. Wireless, battery-operated, fire door retainers can also be used to safely and legally hold fire doors open.
Rated fire doors are tested to withstand an ASTM E119 standard time-temperature curve for a specified period.[8] There are 20, 30, 45, 60, and 90-minute-rated fire doors that are certified by an approved laboratory designated as a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL, e.g., Underwriters Laboratories). The certification only applies if all parts of the installation are correctly specified and installed. For example, fitting the wrong kind of glazing may severely reduce the door's fire resistance period.
Installation[edit]
As well as ensuring the door is hung properly and squarely, it is also very important that where a fire door is installed, any gaps left in the opening between the wall and the door frame must be properly filled with fire resisting material. Fire doors are normally installed by a carpenter. In the UK the British Standard for timber fire door installation is BS 8214: 2016.[9]
Annual inspection[edit]
In the United States, the NFPA requires annual inspections of fire-resistance rated door and frame assemblies.[10] Local Authorities Having Jurisdiction must adopt the new edition for this requirement to take effect. Most jurisdictions in the US will be adopting the IBC (International Building Code) model code, which references the NFPA 80 2007 edition requirement, as their local codes.
NFPA 80 5.2.4.requires the following items shall be verified, at minimum:
According to building and fire codes, annual fire door inspections is the responsibility of the building owner. However, as with other mandatory fire inspections, such as the inspection of fire dampers, the fire door inspections are often omitted and many facilities are out of compliance.[citation needed]
The final say on the acceptance of any inspection requires the approval of the AHJ (Authority Having Jurisdiction).
Modifications[edit]
NFPA 80 includes guidelines concerning field modifications of listed hardware, including frames, builder's hardware, doors, thresholds etc. The growing field of access control and electronic entry systems has resulted in some fire doors being field modified without proper listing agency approval. Field modifications of fire listed assemblies must either be inspected by a listing agency representative, or the modification must be performed by personnel certified to perform such work.[11]
Discover the importance of fire-resistant doors in building safety. Learn about their role in fire prevention, materials used, installation, maintenance, and legal requirements. Enhance safety, energy efficiency, and potentially lower insurance premiums by understanding the benefits and guidelines for fire-resistant doors. Fire-resistant doors are a crucial component in modern building safety. These doors are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, providing occupants with more time to evacuate safely. They are an essential part of a building's passive fire protection system, which works alongside active systems like sprinklers and alarms. Fire-resistant doors are not just about safety; they also contribute to energy efficiency and can impact insurance premiums. Understanding the materials, installation, maintenance, and legal requirements of these doors is vital for building owners and managers. This post delves into the specifics of fire-resistant doors, offering insights into their benefits, materials, installation guidelines, and more. Whether you're a building owner, manager, or simply interested in fire safety, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about fire-resistant doors.
Fire-resistant doors play a pivotal role in enhancing building safety. They are engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke. By compartmentalizing a building, these doors help contain a fire to a specific area, slowing its spread. This containment provides occupants with more time to evacuate safely and allows firefighters to control the blaze more effectively. The doors are typically rated based on the duration they can withstand fire, commonly ranging from 20 minutes to 3 hours. This rating is crucial in determining the level of protection a door offers. Fire-resistant doors also help in maintaining the structural integrity of a building during a fire. By preventing the spread of flames and smoke, they reduce the risk of structural damage, which can be catastrophic. Moreover, these doors are often equipped with smoke seals, which prevent smoke from seeping through gaps. Smoke inhalation is a leading cause of fatalities in fires, making smoke seals an essential feature. In essence, fire-resistant doors are a critical component of a building's passive fire protection system, working alongside active systems like sprinklers and alarms to enhance overall safety.
Fire-rated doors are constructed from materials designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire. Steel is a popular choice due to its strength and durability. It can endure extreme heat without warping, making it ideal for fire-rated doors. Steel doors often have a core made of materials like gypsum or mineral wool, which enhance their fire-resistant properties. Wood is another common material, often used in combination with fire-resistant cores. These cores can be made from materials like vermiculite or intumescent strips, which expand when exposed to heat, sealing gaps and preventing the spread of fire and smoke. Wood doors offer aesthetic appeal while still providing fire resistance. Glass is also used in fire-rated doors, particularly in commercial settings.
Proper installation of fireproof doors is crucial to ensure their effectiveness. The first step is selecting the right door for the specific fire-rating requirements of the building. Once selected, the door must be installed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes. The frame is a critical component of the installation process. It must be securely anchored to the wall to maintain the door's integrity during a fire. Gaps between the frame and the wall should be filled with fire-resistant materials to prevent the spread of smoke and flames. Hinges and hardware must also be fire-rated and installed correctly. This includes using the appropriate number of hinges to support the door's weight and ensure smooth operation. Self-closing devices are often required to ensure the door closes automatically in the event of a fire. Seals and gaskets play a vital role in preventing smoke infiltration. These should be installed around the perimeter of the door and checked regularly for wear and tear. Proper installation is not just about compliance; it's about ensuring the door functions as intended in an emergency, providing safety and peace of mind.
Regular maintenance and inspection of fire-resistant doors are essential to ensure their effectiveness. Start by conducting visual inspections to check for any visible damage or wear. Look for cracks, dents, or warping that could compromise the door's integrity. Check the door's seals and gaskets for signs of wear. These components are crucial in preventing smoke infiltration and should be replaced if damaged. Ensure that the door closes properly and latches securely. A door that doesn't close fully can fail to contain a fire. Fire door inspection services Inspect the hinges and hardware for signs of rust or damage. Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation. Self-closing devices should be tested regularly to ensure they function correctly. It's also important to check the door's fire-rating label. This label provides information about the door's fire resistance and should be legible and intact. If the label is missing or damaged, the door may not be compliant with fire safety regulations. Regular maintenance and inspection not only ensure compliance with safety standards but also provide peace of mind. A well-maintained fire-resistant door is a critical component of a building's fire safety strategy.
Legal requirements for fire doors in commercial buildings are designed to ensure safety and compliance. These regulations vary by region, but there are common standards that most jurisdictions follow. Fire doors must meet specific fire-rating requirements, which indicate the duration they can withstand fire. In many areas, fire doors are required in certain locations, such as stairwells, corridors, and between different occupancy areas. These doors must be self-closing and equipped with fire-rated hardware. The installation must comply with local building codes and standards. Regular inspections are often mandated to ensure fire doors remain in good condition. These inspections check for damage, proper operation, and compliance with fire safety regulations. Documentation of inspections and maintenance is typically required to demonstrate compliance. Fire doors must also be clearly labeled with their fire-rating information. This label provides critical information about the door's fire resistance and must be visible and intact. Compliance with legal requirements is not just about avoiding penalties; it's about ensuring the safety of building occupants and protecting property.
Fire doors play a crucial role in smoke control, an often overlooked aspect of fire safety. Smoke is a leading cause of fatalities in fires, and controlling its spread is vital. Fire doors are designed to prevent smoke from seeping through gaps, containing it to specific areas. Smoke seals are a key feature of fire doors. These seals expand when exposed to heat, filling gaps around the door and preventing smoke infiltration. This containment is critical in providing occupants with a safe escape route and reducing smoke inhalation risks. Fire doors also help maintain visibility in escape routes. By containing smoke, they ensure that corridors and stairwells remain clear, allowing occupants to evacuate safely. This visibility is crucial in preventing panic and ensuring a smooth evacuation. In addition to protecting occupants, smoke control helps minimize damage to property. Smoke can cause significant damage to building contents, and containing it can reduce cleanup and restoration costs. Fire doors are an essential component of a building's smoke control strategy, enhancing safety and reducing risks.
Fire-resistant doors contribute to energy efficiency in several ways. These doors are often designed with insulation properties that help maintain indoor temperatures. By reducing heat transfer, they help keep buildings warm in the winter and cool in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. The materials used in fire-resistant doors, such as steel and composite materials, often have insulating properties. These materials help prevent heat loss, contributing to energy savings. Additionally, fire doors are typically well-sealed, reducing drafts and air leakage. Energy efficiency is not just about cost savings; it's also about sustainability. By reducing energy consumption, fire-resistant doors help lower a building's carbon footprint. This is increasingly important as building owners and managers seek to meet sustainability goals and reduce environmental impact. In essence, fire-resistant doors offer a dual benefit: enhancing safety and contributing to energy efficiency. By investing in these doors, building owners can improve safety standards while also achieving energy savings and sustainability goals.
Fire-resistant and fire-retardant doors are often confused, but they serve different purposes. Fire-resistant doors are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke. They are rated based on the duration they can withstand fire, providing a specific level of protection. Fire-retardant doors, on the other hand, are treated with chemicals that slow the spread of fire. These doors are not designed to withstand fire for a specific duration but rather to delay its spread. They are often used in conjunction with other fire protection measures. The choice between fire-resistant and fire-retardant doors depends on the specific needs of a building. Fire-resistant doors are typically required in areas with higher fire risks, such as stairwells and corridors. Fire-retardant doors may be used in lower-risk areas or as part of a broader fire protection strategy. Understanding the differences between these doors is crucial for making informed decisions about fire safety. Both types of doors play a role in enhancing safety, but their applications and benefits differ.

Choosing the right fire door for your building involves several considerations. Steel fire doors Start by assessing the specific fire risks and requirements of your building. This includes understanding the fire-rating requirements for different areas and the level of protection needed. Local fire door fitters Romford Consider the materials and construction of the door. Steel and composite materials offer durability and strength, while wood provides aesthetic appeal. The choice of material often depends on the design and function of the building. Fire doors should also be equipped with the appropriate hardware and seals. Ensure that the door is self-closing and has fire-rated hinges and locks. Smoke seals are essential for preventing smoke infiltration and should be included in the door's design. Compliance with local building codes and regulations is crucial. Ensure that the door meets the necessary fire-rating requirements and is installed in accordance with legal standards. Consulting with a fire safety professional can provide valuable insights and ensure that the right door is chosen for your building's needs.
Fire doors can have a significant impact on insurance premiums. Insurance companies often consider the level of fire protection in a building when determining premiums. Fire doors enhance safety by preventing the spread of fire and smoke, reducing the risk of damage and loss. By investing in fire doors, building owners can demonstrate a commitment to safety and risk reduction. This can lead to lower insurance premiums, as insurers recognize the reduced risk associated with enhanced fire protection measures. In addition to potential premium reductions, fire doors can also impact insurance claims. In the event of a fire, having fire doors in place can minimize damage and loss, leading to more favorable claim outcomes. This can result in lower out-of-pocket expenses and faster recovery. Overall, fire doors offer a dual benefit: enhancing safety and potentially reducing insurance costs. By investing in these doors, building owners can improve safety standards while also achieving financial savings.
Fire-resistant doors are a vital component of building safety. They prevent the spread of fire and smoke, providing occupants with more time to evacuate. These doors are made from materials like steel, wood, and composite, each offering unique benefits. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to ensure their effectiveness. Legal requirements vary, but compliance is essential for safety and insurance purposes. Fire doors also play a role in smoke control and energy efficiency. Understanding the differences between fire-resistant and fire-retardant doors is important for making informed decisions. Choosing the right fire door involves assessing fire risks and compliance with regulations. Fire doors can also impact insurance premiums, offering potential savings. By investing in fire-resistant doors, building owners can enhance safety, reduce risks, and achieve financial benefits.
Fire-rated doors are vital for building safety, acting as barriers against fire and smoke to protect lives and property. Learn about their features, materials, and maintenance. Fire-rated doors are a crucial component in the safety infrastructure of any building. They are designed to withstand fire and heat, providing a barrier that helps prevent the spread of flames and smoke. These doors are not just about compliance; they are about ensuring the safety of occupants and protecting property. Fire-rated doors are engineered to meet specific standards and are tested rigorously to ensure they perform under extreme conditions. They are a vital part of a building's fire protection system, working alongside alarms, sprinklers, and other safety measures. Understanding the importance and functionality of fire-rated doors can significantly enhance a building's safety profile. Whether in commercial or residential settings, these doors play a pivotal role in safeguarding lives and assets. This post will delve into the key features, materials, installation, and maintenance of fire-rated doors, providing a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to enhance their knowledge or ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Fire-rated doors are designed with specific features that enable them to withstand fire and heat for a designated period. One of the primary features is their ability to resist flames and prevent the spread of fire. This is achieved through the use of materials that can endure high temperatures without compromising structural integrity. Fire-rated doors are equipped with intumescent seals. These seals expand when exposed to heat, filling gaps and preventing smoke and fire from passing through. The door frames are also reinforced to ensure they remain intact during a fire. Another key feature is the door's fire-resistance rating. This rating indicates how long the door can withstand fire, typically ranging from 20 minutes to 3 hours. The hardware used on fire-rated doors, such as hinges and locks, is also fire-resistant. This ensures that the door remains functional during a fire, allowing for safe evacuation. Fire-rated doors are often equipped with self-closing mechanisms. These mechanisms ensure that the door closes automatically after being opened, maintaining the integrity of the fire barrier. Additionally, these doors are tested and certified by recognized authorities to ensure they meet safety standards. Understanding these features is essential for anyone involved in building safety and compliance.
Fire-rated doors play a critical role in enhancing building safety. They act as a barrier, preventing the spread of fire and smoke from one area to another. This containment is crucial in slowing down the progression of a fire, allowing occupants more time to evacuate safely. By compartmentalizing a building, fire-rated doors help to limit damage to property and reduce the risk of injury or loss of life. In addition to containing fire, these doors help in controlling smoke. Smoke inhalation is a leading cause of fatalities in fires, and fire-rated doors are designed to minimize smoke penetration. This is achieved through the use of intumescent seals and other smoke control features. By keeping smoke contained, these doors improve visibility and air quality in escape routes, facilitating safer evacuations. Fire-rated doors also contribute to the overall fire protection strategy of a building. They work in conjunction with other safety systems, such as alarms and sprinklers, to provide a comprehensive safety net. By maintaining the integrity of fire-rated compartments, these doors help ensure that other fire protection measures can function effectively. In essence, fire-rated doors are a vital component of any building's safety infrastructure.
Fire-rated doors are constructed from materials specifically chosen for their fire-resistant properties. Steel is one of the most common materials used. It is highly durable and can withstand extreme temperatures without losing its structural integrity. Steel doors are often used in commercial and industrial settings due to their strength and resilience. Wood is another material used in fire-rated doors, although it is typically treated with fire-retardant chemicals. These chemicals enhance the wood's ability to resist fire, making it suitable for use in fire-rated doors. Wood doors are often preferred in residential settings for their aesthetic appeal. Glass is also used in fire-rated doors, particularly in settings where visibility is important. Fire-rated glass is specially treated to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames. It is often used in combination with other materials to provide both safety and visibility. Composite materials, which combine different elements, are also used in fire-rated doors. These materials are engineered to provide optimal fire resistance while maintaining other desired properties, such as weight and appearance. Understanding the materials used in fire-rated doors is essential for selecting the right door for a specific application.
Fire door ratings and classifications are essential for understanding the level of protection a door provides. These ratings indicate how long a door can withstand fire and heat, typically measured in minutes or hours. Common ratings include 20, 45, 60, 90, and 180 minutes. The rating is determined through rigorous testing, where the door is exposed to fire conditions to assess its performance. The classification of fire doors is based on several factors, including the materials used, the door's construction, and its intended use. For example, some doors are classified as smoke doors, designed to prevent the spread of smoke in addition to fire. Others may be classified based on their location within a building, such as corridor doors or stairwell doors. Understanding these ratings and classifications is crucial for ensuring compliance with safety regulations. It helps in selecting the appropriate door for a specific application, ensuring that it provides the necessary level of protection. FD60 fire doors Fire door ratings and classifications are a key component of a building's fire safety strategy, providing valuable information for architects, builders, and safety professionals.
Proper installation of fire-rated doors is critical to their effectiveness. The installation process must adhere to specific guidelines to ensure the door performs as intended during a fire. One of the primary requirements is that the door must be installed in a fire-rated frame. This ensures that the entire assembly can withstand fire and heat. The door must be hung with fire-rated hardware, including hinges, locks, and closers. These components are designed to maintain their integrity under fire conditions, ensuring the door remains functional. The gap between the door and the frame must be within specified limits to prevent the passage of smoke and flames. Intumescent seals must be properly installed around the door's perimeter. These seals expand when exposed to heat, filling gaps and preventing the spread of fire and smoke. The door must also be equipped with a self-closing mechanism to ensure it closes automatically after being opened. Compliance with local building codes and regulations is essential during installation. This ensures that the door meets all safety requirements and provides the necessary level of protection. Proper installation is a critical step in ensuring the effectiveness of fire-rated doors.
Regular maintenance and inspection of fire-rated doors are essential to ensure their effectiveness. These doors must be kept in good working condition to provide the necessary level of protection during a fire. One of the primary maintenance tasks is to regularly check the door's hardware. This includes inspecting hinges, locks, and closers for signs of wear or damage. Any faulty components should be replaced immediately to ensure the door remains functional. The door's seals should also be inspected regularly. Intumescent seals must be intact and free from damage. These seals play a crucial role in preventing the spread of fire and smoke, so any issues should be addressed promptly. The door's self-closing mechanism should be tested to ensure it operates correctly. This mechanism is essential for maintaining the integrity of the fire barrier. Regular inspections should be conducted to ensure the door complies with safety regulations. This includes checking the door's fire rating and ensuring it is appropriate for its location. Any modifications to the door or its surroundings should be assessed to ensure they do not compromise its effectiveness. Proper maintenance and inspection are key to ensuring the reliability of fire-rated doors.
Legal requirements for fire-rated doors in commercial buildings are designed to ensure the safety of occupants and property. These requirements vary by location but generally include specific guidelines for the installation, maintenance, and inspection of fire-rated doors. One of the primary legal requirements is that fire-rated doors must be installed in areas where fire separation is necessary. This includes corridors, stairwells, and other critical areas. The doors must meet specific fire-resistance ratings, which indicate how long they can withstand fire and heat. These ratings are determined through testing and certification by recognized authorities. The doors must also be equipped with fire-rated hardware, including hinges, locks, and closers. Regular inspections are required to ensure the doors remain in compliance with safety regulations. This includes checking the door's condition, hardware, and seals. Any modifications to the door or its surroundings must be assessed to ensure they do not compromise its effectiveness. Compliance with legal requirements is essential for ensuring the safety of occupants and protecting property in commercial buildings.

Fire-rated doors differ from regular doors in several key ways. One of the primary differences is their ability to withstand fire and heat. Fire-rated doors are constructed from materials that can endure high temperatures without losing their structural integrity. This is in contrast to regular doors, which may not provide the same level of protection. Fire-rated doors are equipped with intumescent seals, which expand when exposed to heat. These seals prevent the spread of fire and smoke, a feature not typically found in regular doors. The hardware used on fire-rated doors, such as hinges and locks, is also fire-resistant. This ensures that the door remains functional during a fire, allowing for safe evacuation. Another key difference is the presence of a fire-resistance rating.
Fire-rated doors play a crucial role in smoke control, which is essential for ensuring the safety of building occupants. Smoke inhalation is a leading cause of fatalities in fires, and controlling its spread is vital. Fire-rated doors are designed to minimize smoke penetration through the use of intumescent seals. These seals expand when exposed to heat, filling gaps and preventing smoke from passing through. By containing smoke, fire-rated doors help maintain visibility and air quality in escape routes. This is essential for facilitating safe evacuations, as smoke can obscure vision and make it difficult for occupants to find their way to safety. The containment of smoke also helps protect property by preventing smoke damage to areas not directly affected by the fire. Fire-rated doors are often used in conjunction with other smoke control measures, such as smoke curtains and ventilation systems. Together, these measures provide a comprehensive approach to smoke control, enhancing the overall safety of a building. Understanding the role of fire-rated doors in smoke control is essential for anyone involved in building safety and compliance.
Fire-rated doors are a critical component of emergency evacuation plans. They play a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient evacuation of building occupants during a fire. By containing fire and smoke, these doors help maintain clear and safe escape routes. This is essential for allowing occupants to evacuate quickly and safely. Fire-rated doors are strategically placed in areas where fire separation is necessary, such as corridors and stairwells. This placement helps to compartmentalize a building, slowing down the progression of a fire and providing more time for evacuation. The doors are equipped with self-closing mechanisms, ensuring they close automatically after being opened. This maintains the integrity of the fire barrier and prevents the spread of fire and smoke. In addition to their role in containment, fire-rated doors are often used in conjunction with other safety measures, such as alarms and sprinklers. Together, these measures provide a comprehensive approach to fire safety, enhancing the overall effectiveness of an emergency evacuation plan. Fire door inspection services Understanding the role of fire-rated doors in evacuation plans is essential for ensuring the safety of building occupants.
Fire-rated doors are an essential part of any building's safety infrastructure. They provide a critical barrier against fire and smoke, protecting both lives and property. Understanding their features, materials, and installation requirements is key to ensuring their effectiveness. Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for keeping these doors in good working condition. Compliance with legal requirements is essential for ensuring safety in commercial buildings. By playing a vital role in smoke control and emergency evacuation plans, fire-rated doors enhance the overall safety of a building. Their importance cannot be overstated, making them a crucial consideration for anyone involved in building safety and compliance.
Yes, fireproof sliding doors are designed to maintain compartmentalization and fire resistance while allowing space-saving operation.
Some fireproof doors also offer sound insulation, but not all do. Check for dual-rated models that offer both fire and soundproofing.
Look for doors certified to UL, BS 476, EN 1634, or NFPA standards, depending on your country’s building codes.
Yes, they are especially important in multi-story homes or those with attached garages, to slow fire spread and provide safe exit time.
Most fire resistant doors are rated for 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes of protection, depending on their certification.